Introduction #
WordPress has several features that allow content creators to maximise the impact of their work. This guide contains details of the following features:
Columns #
WordPress allows the use of columns. This allows pages to be laid out in multiple columns, as is commonly found in newspapers etc. However, care must be taken to ensure readability is maintained. The use of columns is recommended if you are laying out a page in a “tabular style”
From the block editor, select Columns, and from the options select a predefined one, two or three-column layout. If more than three columns are required, an additional plugin will be required.
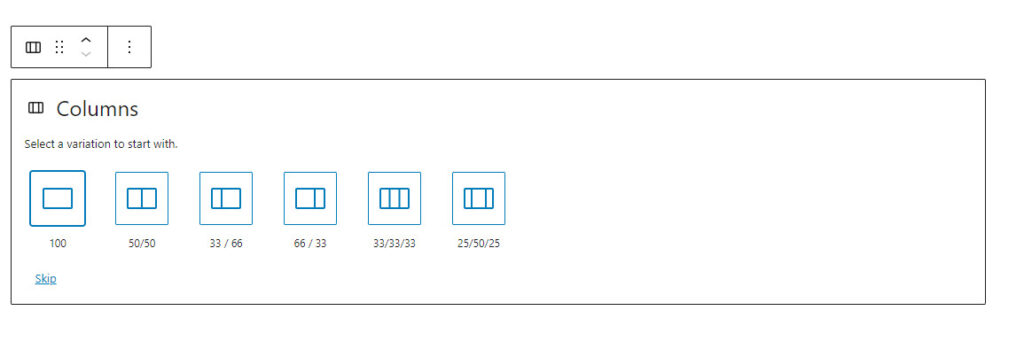
If the 33/33/33 option is selected, the result is:

The Column toolbox gives the following options from left to right:
- Select the parent Columns block.
- Move the column
- Align the columns
- Other options
It should be noted that it is possible to stack columns on a mobile device, using the option in the Settings Toolbar
The size of individual columns can be adjusted by the required column, and adjusting the width, in the Settings option, in the right-hand sidebar. While a number of units are provided, it is recommended that % is used, this ensure that the sum of all the columns does not exceed 100%
Once the basic column layout is selected, text and images can be entered into each column by using the block editor. In the editing view, an empty column is highlighted as a dotted box as shown above.

In the above example, three columns of equal size are shown, where:
- Column one contains an image above a Paragraph block.
- Column two contains a button, linking to a group page
- Column three, a two × two table
The options that can be applied to a column include:
- Settings:
- If blocks are nested with a column, the content width of the nested blocks can be controlled.
- Adjust the width and justification.
- Style
- Text and background colour
- Padding and margin adjustment
- Addition of a block border
The Column (i.e., child) Block Toolbar can be accessed from the Columns (I.e., parent) block toolbar as required.
Spacer #
The Spacer block, allows authors to place a white block into the text to aid the reader. In the editing view example below, a spacer (100px in depth) is being added between two paragraphs. White space should not be considered wasted space, but an important addition to readability.

The Spacer block’s height can be controlled by using the settings sidebar.
Grid layout #
The Grid Layout allows the content provider to arrange blocks in a grid, similar to the Group, Row and Stack blocks. On selecting the Grid Block, the basic grid is made available:

The content provider has the option of Manual or Auto setting under type, it should be noted there are significant differences between the two options:
- In Manual, the number of columns across the screen is defined. In the above example, the three columns will be displayed irrespective of screen width. This may lead to significant accessibility issues when the page visitor uses a mobile phone.
- In Auto, the width of the column is defined (in pixel, rem or em). For a three-column display, the width is typically between 260 and 310 px, depending on the block spacing (set in the styles options). When displayed on a screen with a reduced resolution, columns are stacked. It is recommended that the Auto option is always used
The Advanced settings allow the setting of an HTML Anchor. The Style pane provides options for text and background colours, adding a background image, setting the margins, padding and block spacing, and if required minimum row height.
To enter content, select the content block using block inserter icon in the left-hand column, and enter the required content. To enter the next column, ensure that the grid is selected, using the breadcrumbs, select the block inserter icon and then insert the block required followed by its content Continue the process until the grid is complete. The addition of further rows is handled automatically.
In the case of the Paragraph block, there is an option that allows the block to extend over one or more columns or rows, this is found in the Paragraph settings under Grid Span. As noted above this has implications for accessibility on mobile phones.
The following grid consists of a paragraph, image and list in the first row, then an image and a paragraph spanning two columns in the second row:

Once the grid has been populated it can be formatted, to give the following:
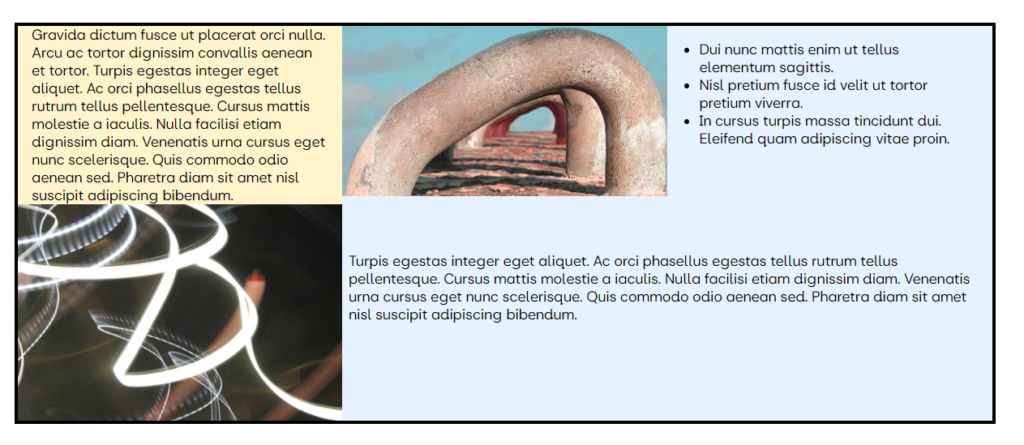
Given the possible formatting options available in individual blocks and the grids, a considerable number of display options exist, In this case, the following formatting has been applied:
- Grid:
- Auto type, with 300px width.
- Block spacing set to zero, in style
- Very Light Blue background.
- 4 px black border added
- Top left paragraph.
- Very Light Yellow Background
- No padding: top and bottom.
- “Small” padding left and right.
- Top Middle Image
- Standard Image Block
- Top Right List
- “Small” padding: top and bottom.
- “Large” padding: left and right, if this is not applied the list’s dot will appear outside the grid boundaries.
- No background colour was selected (i.e. left transparent to see the grid background colour)
- Bottom Left Image.
- Standard Image Block used
- Bottom Right Paragraph.
- Column span set to 2, row span set to 1. These settings are found in the paragraph’s block settings pane on the Right Hand Side.
- “2 X” padding on the top and bottom.
- No padding was added on the left or right.
- No background colour was selected.
Separator #
The Separator block allows a fixed-width line to be placed between blocks, the line, can either be short or wide and in any colour of the u3a palette. A separator can be used to separate ideas within a piece of text, to improve readability. By selecting Dimensions in the style sidebar, the wide space above and below the line can be adjusted either linked or separately, as shown below three separator options are available:

Page Break #
In a limited number of cases a page may become excessively long, for example, a report of a meeting or a visit report, and for ease of viewing you wish to split it into two or more pages. While a number of separate WordPress pages could be authored and linked together, a more convenient approach, for both the visitor and author is to use the Page Break block. This block effectively splits the single page into multiple sub-pages for the visitor. If the page break is inserted, the following is displayed:
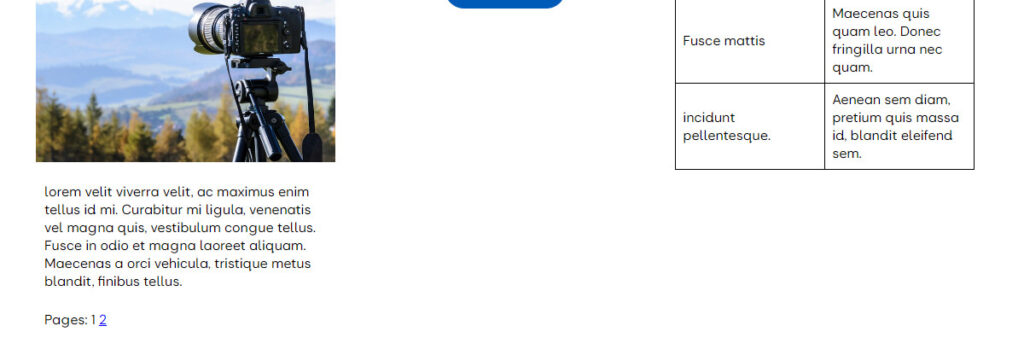
By selecting 2, the visitor is taken to the second part of the page. In addition, the visitor can toggle between the “pages” with ease
Time to Read and Work Count #
Two additional blocks can be added to a page for information:
- A Time to Read block can be added, which provides the content creator and visitor with an indication of the time to read a page, based on 200 words per minute.
- A Word Count block can be added





